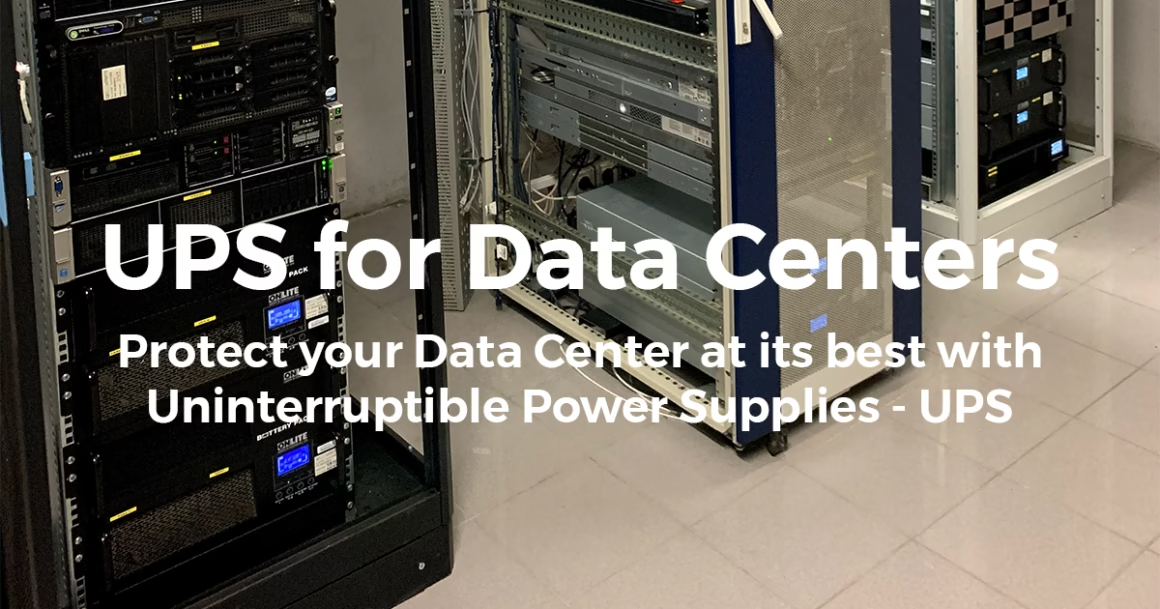
UPS for Data Centers: Introduction
Protecting data centers is a top priority for any organization that manages critical IT infrastructure. Among the main threats, power outages pose a significant risk, potentially leading to data loss, equipment damage, and operational disruptions. An Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) system, also known as a “Gruppo di Continuità” (UPS), is an essential tool for ensuring operational continuity and equipment protection.
What does the acronym UPS stand for?
UPS stands for Uninterruptible Power Supply. It is a device that provides temporary power during an outage or voltage drop, ensuring continuous operation of critical electronic equipment such as computers, servers, or industrial systems. In addition to preventing sudden interruptions, the UPS protects connected devices from damage caused by voltage fluctuations or overloads, making it an essential solution for both home and business environments.
What is a Data Center?
A data center is a physical or virtual facility designed to house and manage large amounts of data and IT applications. It acts as the technological heart of an organization, providing essential infrastructures such as servers, storage systems, networks, and security. Data centers ensure the efficient and secure processing, storage, and distribution of data, making them critical for online services, business applications, and cloud platforms. With advanced cooling, power, and redundancy technologies, they ensure high availability and operational continuity, even in the event of failures or emergencies.
How many Data Centers are there in Italy?
In Italy, there are currently around 29 operational data centers, with an expected increase to 31 in the coming years, thanks to growing digitization and the demand for computing infrastructure. The main areas of concentration are Lombardy, with Milan as the primary hub, and Lazio, with Rome emerging as a second strategic center. The Italian data center market is experiencing significant growth, with investments estimated at up to 15 billion euros by 2025. However, challenges related to regulations and electrical infrastructure remain, necessary to support the construction of hyperscale data centers, which exceed 10 MW of power.
However, this is only part of the technological landscape in our country. Many medium-to-large businesses, despite the evolution of cloud solutions and the availability of colocations in large data centers, continue to manage their own corporate data centers internally. These infrastructures, often custom-built to meet the specific needs of the organization, play a crucial role in managing critical applications, sensitive data, and operational processes.
The Risks of an Unprotected Data Center
- Data Loss: A sudden power interruption can compromise data in transit, especially during write operations on disks.
- Hardware Damage: Voltage fluctuations or blackouts can damage servers, storage systems, and network devices, leading to high replacement costs.
- Operational Downtime: Loss of access to IT systems can halt business operations, causing significant economic impact and potential reputational damage.
- Security Impact: Some security systems, such as firewalls or cameras, may shut down during an outage, exposing the infrastructure to additional risks.
Solutions for Protection with UPS
Implementing a UPS requires a well-thought-out strategy that takes into account the needs of the data center and available resources. Here are the two main protection architectures:
1. Centralized Protection
In this configuration, a single UPS system is used to protect the entire data center.
Advantages:
- Simplified management: One point of monitoring and maintenance.
- Energy efficiency: Greater control over energy delivery.
- Adaptability: Can be expanded with additional, more powerful UPS modules.
Disadvantages: - High initial cost: Significant investment is required for a high-capacity UPS.
- Single point of failure: If the centralized UPS fails, it can compromise the entire protection system.
2. Distributed Protection
In this configuration, each server or critical device group is protected by a dedicated UPS unit.
Advantages:
- Flexibility: The UPS can be tailored to the specific needs of each component.
- Redundancy: Failures in a single UPS will not compromise the entire system.
Disadvantages: - Complex management: A larger number of devices to monitor and maintain.
- Space and operational costs: Requires more UPS units, increasing both footprint and energy consumption.
Our Solutions to Protect Your Data Center
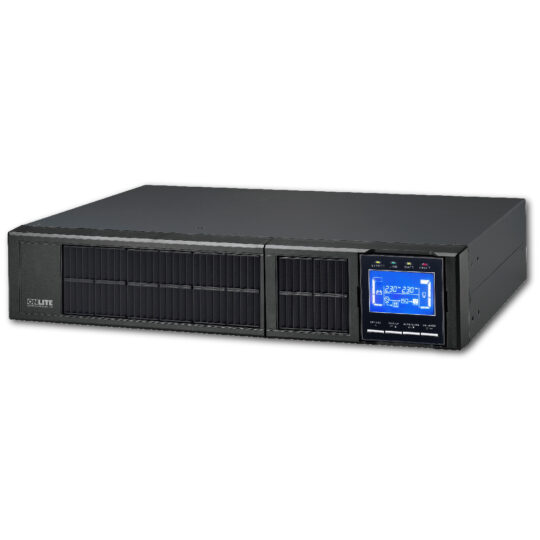
For years, ON LITE S.r.l. has been offering market solutions to protect data centers, with highly reliable UPS systems that help prevent service interruptions.
For data center protection of any size, we recommend products from the SKUDO ONE line, featuring On-Line Double Conversion technology, the only viable alternative when data loss could have irreparable consequences.
Conclusion
An Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) is essential for ensuring the continuity and security of data centers. The choice between centralized and distributed protection depends on various factors, such as the size of the infrastructure, the available budget, and redundancy requirements. Investing in UPS solutions is not just a technical choice, but a strategic decision that can safeguard the operational heart of an organization.
Choosing a reliable and competent partner, such as ON LITE S.r.l., with nearly 30 years of experience, for the design and implementation of the protection system is crucial to ensure that the data center can operate safely and without interruptions, regardless of external conditions.


Leave a Reply